- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
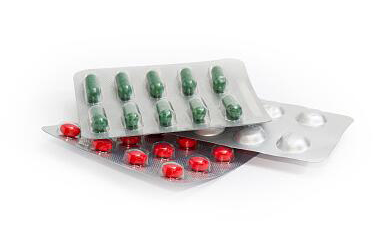
The core monomer of PVDC
2025-09-09
Vinylidene chloride, also known as VDC, has a structural formula of Cl₂CCH₂ and a CAS number of 75-35-4. Due to its chemical nature, VDC readily undergoes polymerization, addition, chlorination, and decomposition reactions. As the primary monomer used in the production of polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), VDC is widely applied in the pharmaceutical, dye, and other industrial sectors.
As the core monomer of PVDC, VDC significantly influences the structure and properties of the resulting resins. Its main functions include:
• Serving as the primary monomer in Polymer materials: VDC constitutes more than 80% of the resin formulation and is copolymerized with other monomers, such as vinyl chloride or acrylates, through emulsion polymerization to form the polymer backbone.


• Imparting high barrier properties: The symmetrical molecular structure and high crystallinity of VDC endow PVDC resins with excellent barrier properties against oxygen and water vapor. The low oxygen permeability coefficient of the resulting polymer makes it particularly suitable for use in anti-corrosion coatings and packaging materials.
• Enabling water-based processing: By employing polymerization techniques, VDC monomers can react with other components to form water-based emulsions, thereby reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, complying with environmental regulations, and enhancing application compatibility in coating formulations.
• Enhancing functional performance: The inherent chemical characteristics of VDC confer oil resistance, mildew resistance, heat shrinkage resistance, and printability to the resin, thereby expanding its application across various fields, including food packaging, fibers, coatings, and adhesives.
Whether you’re developing any sustainable packaging, Aosen provides a full range of polymer materials to bring your vision to life.
Contact us today to learn how Aosen’s advanced polymer solutions can drive innovation in your business.